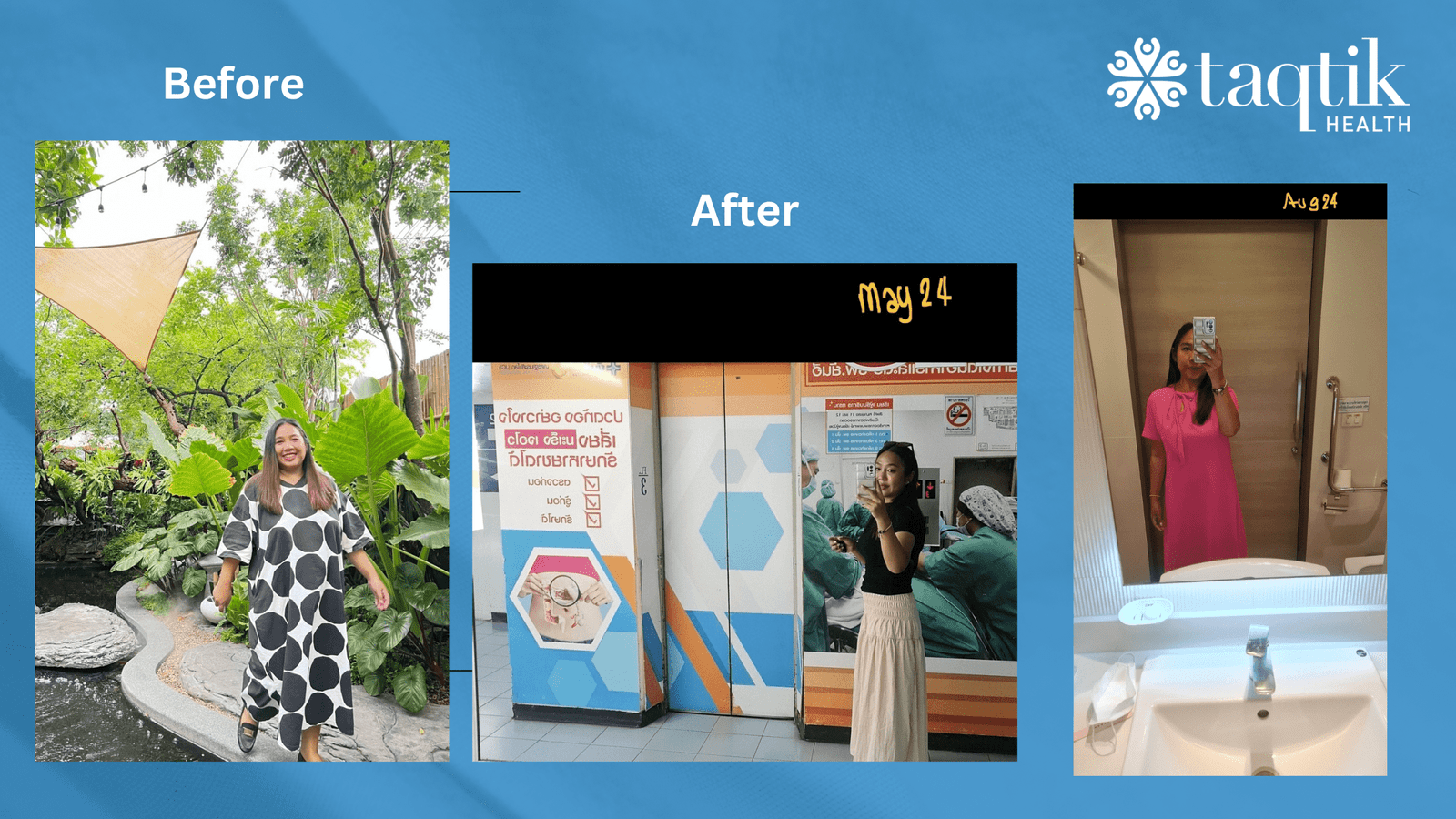
Post-Bariatric and GLP-1 Post-Care to Maximize Results
Post-Bariatric and GLP-1 Post-Care to Maximize Results | Taqtik Health
Introduction
Undergoing bariatric surgery or starting GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) agonist treatments like semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy) or tirzepatide (Mounjaro, Zepbound) is a major step toward long-term weight loss and improved metabolic health. But these treatments are only part of the journey. What you do after surgery or while on GLP-1 therapy is just as important as the procedure itself. Post-care plays a crucial role in maximizing results, minimizing complications, and supporting a sustainable transformation.
At Taqtik Health, we specialize in comprehensive post-care support tailored to each individual. Whether you are a bariatric surgery patient or using GLP-1 medications, this guide will walk you through proven strategies to get the most out of your health investment.
Why Post-Care Matters
Many patients believe the hardest part is over once they undergo surgery or begin GLP-1 treatment. However, long-term success depends on what follows. Without proper follow-up care, many patients experience weight regain, nutritional deficiencies, or stalled progress. Post-care ensures:
- Sustained weight loss
- Muscle preservation
- Prevention of nutrient deficiencies
- Mental health and emotional support
- Long-term lifestyle changes
1. Nutrition Support: Building a Foundation for Success
Both bariatric surgery and GLP-1 medications alter how your body processes food. Post-care should include ongoing nutritional counseling to ensure your body is fueled for recovery and long-term health.
Post-Bariatric Nutrition:
- Start with a liquid diet, then transition to pureed, soft, and eventually solid foods.
- Focus on protein intake (60-80g/day initially)
- Avoid sugar, alcohol, and carbonated drinks
- Take prescribed vitamins (B12, iron, calcium, vitamin D)
GLP-1 Nutrition:
- Eat smaller, protein-rich meals to manage appetite
- Stay hydrated and avoid greasy or high-fat foods to reduce nausea
- Work with a dietitian to identify trigger foods and optimize satiety
Taqtik Health provides dietitian check-ins to ensure you're hitting nutritional milestones.
2. Physical Activity: Rebuilding Strength and Endurance
Exercise is vital for weight maintenance, lean muscle preservation, and mental health.
Post-Bariatric:
- Start walking as early as the day after surgery
- Gradually increase to 150 minutes/week of moderate activity
- Incorporate resistance training after 6–8 weeks
GLP-1 Users:
- Walking and strength training enhance insulin sensitivity
- Exercise offsets potential muscle loss from rapid weight reduction
- Regular movement can reduce gastrointestinal side effects
Taqtik clients receive personalized movement plans via our mobile app and virtual coaching.
3. Emotional and Mental Health Support
Rapid body changes and hormonal shifts can lead to emotional distress. Depression, anxiety, or disordered eating can emerge post-procedure or during medication use.
Support Strategies:
- Join virtual support groups through Taqtik Health
- Access licensed therapists for body image and emotional eating issues
- Practice mindfulness, journaling, or meditation
Our community platform gives patients a safe space to connect and share experiences.
4. Monitoring Biometrics and Health Indicators
Keeping track of physical and biochemical markers is essential. Regular monitoring helps identify early warning signs and reinforce progress.
What to Track:
- Weight and BMI
- Blood pressure
- Blood sugar (HbA1c)
- Lipid panels
- Liver and kidney function
- Lean muscle mass vs. fat mass
Taqtik’s Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) program includes wearable syncing, monthly check-ins, and physician reviews to keep your care team informed.
5. Medication Adherence and Supplementation
Consistency is key. Patients must take GLP-1 injections as prescribed or bariatric supplements daily.
Taqtik’s Medication Support:
- Refill reminders and tracking tools
- Education on side effect management
- Telehealth check-ins for dosage adjustments
For post-surgical patients, we offer a vitamin subscription service to simplify compliance.
6. Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Understanding what to avoid is just as important as knowing what to do.
Post-Bariatric Pitfalls:
- Grazing throughout the day
- Skipping supplements
- Drinking fluids with meals
- Ignoring signs of dumping syndrome
GLP-1 Pitfalls:
- Skipping meals
- Overestimating what medications can do alone
- Neglecting exercise and stress management
Our educational modules cover these risks and provide proactive strategies.
7. Tailored Follow-Up Schedule
Taqtik Health follows best practices for structured follow-up:
Bariatric Care Plan:
- Weekly support check-ins during first month
- Monthly clinical reviews (up to 12 months)
- Annual surgical follow-ups with bloodwork
GLP-1 Care Plan:
- Bi-weekly coaching for 3 months
- Monthly medication reviews
- Quarterly labs and health coaching
8. Community and Peer Support
You’re more likely to stay committed when you feel connected. Peer accountability matters.
Taqtik’s member-exclusive forums and ambassador-led challenges make it easier to stay motivated. Whether celebrating a "non-scale victory" or sharing a setback, you're never alone.
Join our community: Taqtik Health Community Platform
9. Transitioning to Maintenance Mode
Eventually, the intense phase of weight loss slows down. That’s when relapse risk is highest.
Maintenance Tips:
- Set realistic weight maintenance goals
- Shift from calorie deficit to nutrient balance
- Continue strength training
- Prioritize sleep and stress reduction
Taqtik provides annual wellness assessments to recalibrate your plan.
Transform Results Into Lifelong Change
Surgery or medication might be the spark, but the journey doesn’t stop there. Post-care is where transformation becomes sustainable. With Taqtik Health, you're not just a patient — you're a partner in your wellness journey. Our wraparound care model ensures you stay supported, accountable, and informed at every step.
Ready to transform your outcome into a lifestyle? Start your post-care journey with Taqtik today.